Introduction to UX Design
User experience (UX) design plays a crucial role in crafting websites and applications that resonate with users. UX means understanding user needs and enhancing the interaction between users and products. UX design is the art of creating a meaningful interaction by fulfilling user expectations.
The aim is to maximise usability, accessibility, and enjoyment during interaction. UX design ensures that a product extends beyond mere functionality to become both engaging and intuitive, elements imperative for a triumphant digital experience.
Key Concepts of UX vs UI Design
Definition of UX and UI
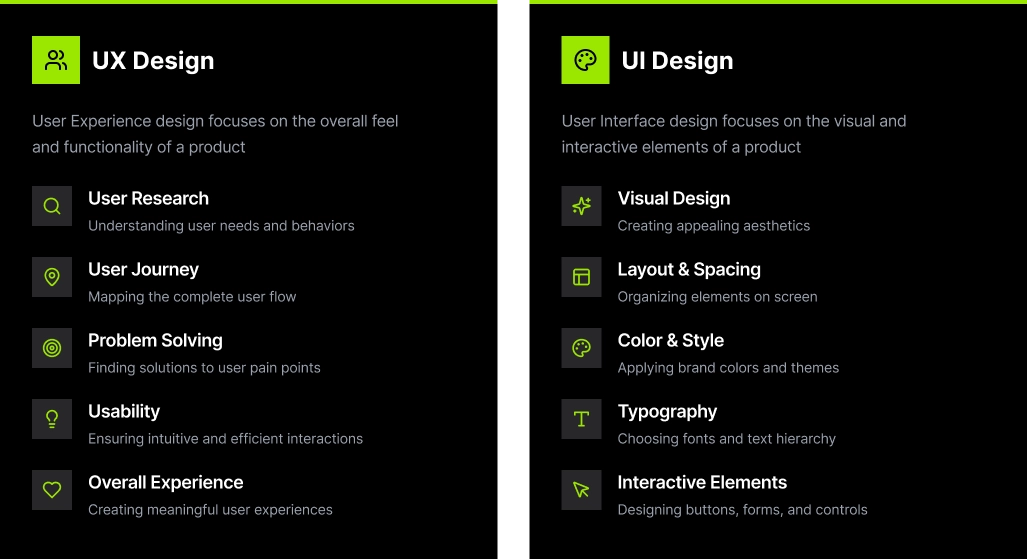
UX design involves enhancing users' overall experience by improving their interaction with a product. UI design concerns the product’s interface, concentrating on aesthetics and responsiveness.
Differences and Similarities
While UX concentrates on the comprehensive experience, UI emphasises the visual components. Both are indispensable but serve distinct functions. UI design pertains to aesthetics and interactivity, whereas UX design revolves around the user’s journey.
The UX Design Process Explained
Research and Analysis
Research serves as the cornerstone of UX design. Employing techniques such as surveys, interviews, and usability testing assists in data collection. Analysis of this data unveils user needs and expectations, enabling designers to formulate relevant solutions.
Through tools like personas and user journey maps, designers can visualise the user’s interaction flow and identify improvements. This analysis sets the groundwork for informed design decisions.
Design and Prototyping
Upon concluding the research phase, designers embark on sketching and prototype development. Prototypes serve as visual representations that facilitate early user feedback and iterative modifications, ensuring the design aligns with user needs.
Techniques like wireframing and interactive prototyping enable designers to explore different solutions before arriving at a final design. This iterative approach mitigates risks and promotes user-centred innovation.
Testing and Iteration
Testing encompasses verifying the prototype’s functionality with real users, collecting feedback, and enacting needed adjustments. Iteration is paramount, enabling continuous refinement until the final product conforms to quality standards.
User testing should be a continuous process, even after the product’s launch, to ensure ongoing improvements. Encouraging user feedback through surveys and metrics helps in making informed updates.

The Role of a UX Designer
Skills Required
A UX designer must wield various skills, including empathy, problem-solving, and technical acumen. Proficiency with tools like Adobe XD and Sketch is vital, alongside soft skills like communication and collaboration.
In addition to these, an understanding of psychology and human behaviour can greatly enhance a designer’s ability to create user-centric experiences. Continuous learning and adapting to new tools and methodologies are also key to staying relevant in this dynamic field.
Benefits of Good UX Design
Improved User Satisfaction
Effective UX design directly influences user satisfaction. When users find products easy to navigate and enjoyable, their overall experience is elevated. This satisfaction fosters increased loyalty and repeat interaction.
Satisfied users are more likely to recommend products to others, creating a ripple effect that can substantially amplify a brand’s reach and reputation.
Increased Engagement and Conversion
Well-implemented UX design enhances engagement by making interactions pleasurable and intuitive. This often translates to higher conversion rates, as users are more inclined to perform desired actions, such as purchasing or signing up.
Incorporating features like personalised recommendations and streamlined checkout processes can further enhance conversion rates, turning casual users into loyal customers.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding UX in design is crucial for crafting user-friendly products.
- UX design involves researching user needs and creating intuitive product interactions.
- Integrating UX and UI design strategies results in cohesive and appealing digital experiences.
- A well-defined UX design process ensures products meet user expectations and business goals.
- Key principles like simplicity and feedback enhance user interaction.
- Constant user testing and feedback strengthen product development.
- Developing relevant skills equips designers for success in a fast-evolving field.
For more insights, explore our article on technical SEO and its impact on UX, which details how optimising technical aspects can improve user experiences.



